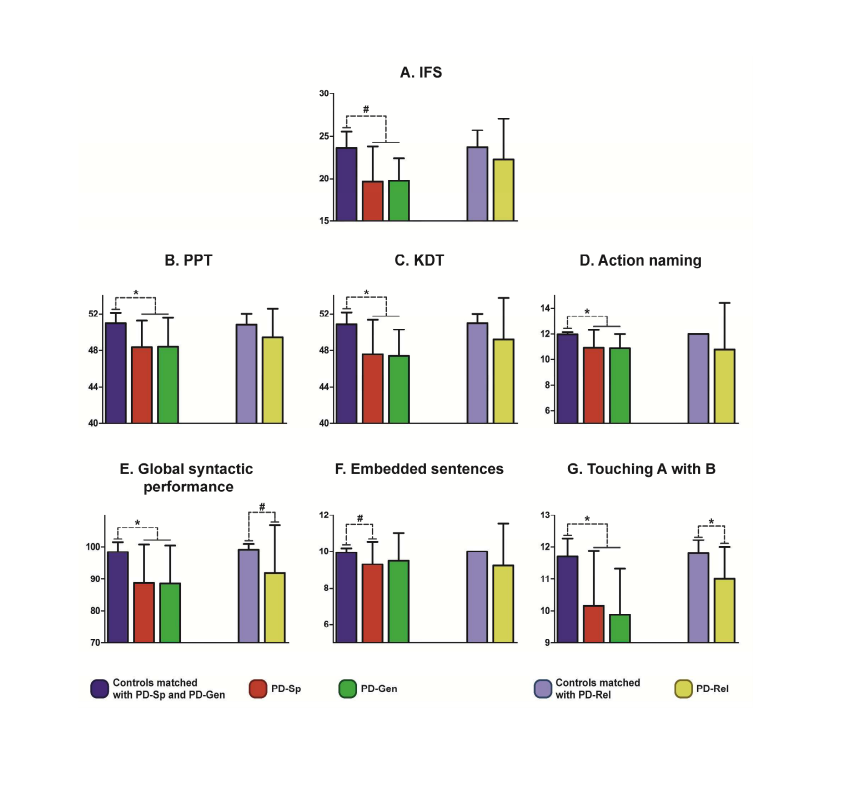
Objective: The worldwide spread of Parkinson’s disease (PD) calls for sensitive and specific measures enabling its early (or, ideally, preclinical) detection. Here we employ language measures revealing deficits in PD to explore whether similar disturbances are present in asymptomatic individuals at risk for the disease. Methods: We administered executive, semantic, verb-production, and syntactic tasks to sporadic PD patients, genetic PD patients with parkin (PARK2) or dardarin (LRRK2) mutation, asymptomatic first-degree relatives of the latter with similar mutations, and socio-demographically matched controls. Moreover, to detect sui generis language disturbances, we ran ANCOVA tests using executive functions as covariate. Results: The two clinical groups showed impairments in all measures, most of which survived covariation with executive functions. However, the key finding concerned asymptomatic mutation carriers. While these subjects showed intact executive, semantic, and action-verb production skills, they evinced deficits in a syntactic test with minimal working memory load. Conclusions: We propose that this sui generis disturbance may constitute a prodromal sign anticipating eventual development of PD. Moreover, our results suggest that mutations on specific genes (PARK2 and LRRK2) compromising basal ganglia functioning may be subtly related to language-processing mechanisms.
Keywords: sporadic Parkinson’s disease, genetic Parkinson’s disease, PARK2, LRRK2, preclinical mutation carriers, language.